As organizations increasingly rely on mobile devices for business, safeguarding sensitive corporate data on personal and company-owned Android devices has become critical. Microsoft Intune Application Protection Policy (APP) provides a robust framework to protect applications and their data without requiring full device management. This article explores the features, benefits, and setup of Microsoft Intune’s application protection policies for Android, helping enterprises secure their mobile workforce efficiently.
Table of Contents
1. What is an Application Protection Policy (APP)?
Application Protection Policies in Microsoft Intune focus on securing the data within mobile apps used for business whether mobile devices are enrolled (MDM + APP) or non-enrolled to Microsoft Intune (APP only).
The policies ensure that only managed applications (e.g. Microsoft Outlook, Teams, OneDrive or 3rd party Apps) comply with security rules. If users attempt to access corporate data via these apps, the policy ensures the data remains protected, even if the device is not enrolled in mobile device management (MDM).
2. Example Use Cases
1. BYOD Employee Scenario:
An employee uses a personal Android phone to access both personal and corporate email on Microsoft Outlook. An APP ensures corporate emails are encrypted, prohibits copy-pasting to personal apps, and forces employees to set and use separate PIN when accessing Corporate Apps.
2. Lost or Stolen Device:
If an employee loses their Android device, a selective wipe can remove only corporate data while keeping personal information intact.
3. Data Sharing Restrictions:
The company allows employees to collaborate using OneDrive and Microsoft Teams but blocks saving files to non-corporate cloud services like Google Drive.
3. Setting Up Application Protection Policies for Android
Follow these steps to create and deploy an Application Protection Policy in Intune:
1. Log in to Microsoft Intune
2. Create a New Policy – Go to Apps > App Protection Policies > Create Policy – Select Android as the platform.
From App List you have the option to target APP to All Apps (Microsoft + 3rd Party Apps)
Or to All Microsoft Apps Or to Core Microsoft Apps only.

You have the option to select Public Apps based on your needs.
Or if you have LOB App (Private App, developed for your organization only) can be added to Custom App List on one condition. App MUST be integrated with Intune-MAM SDK or wrapped with Intune Wrapping Tool per Microsoft Article

3. Configure Policy Settings:
Define Send Org Data (Where Corporate App will send data (share) to.
Save Copies of Corporate Data (e.g. OneDrive only or OneDrive and Local Drive.. etc.)
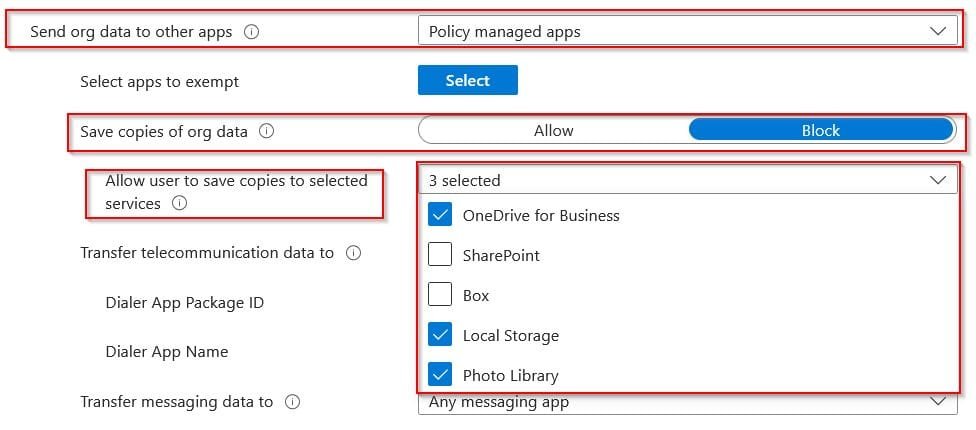
Receive Data from Other Apps (Where Corporate Apps will receive share from)
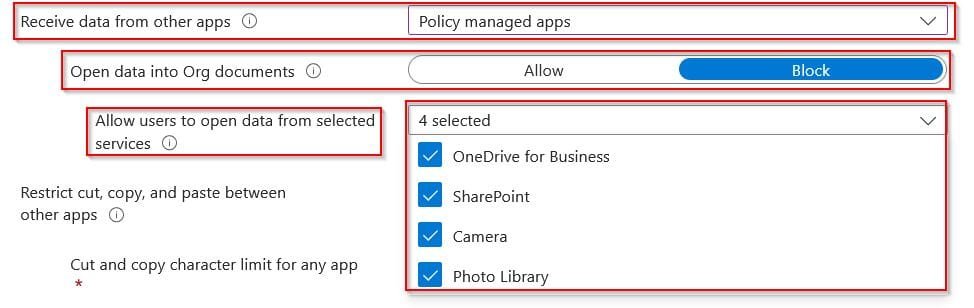
Encrypt Organization Data (to encrypt local data on all corporate Apps)

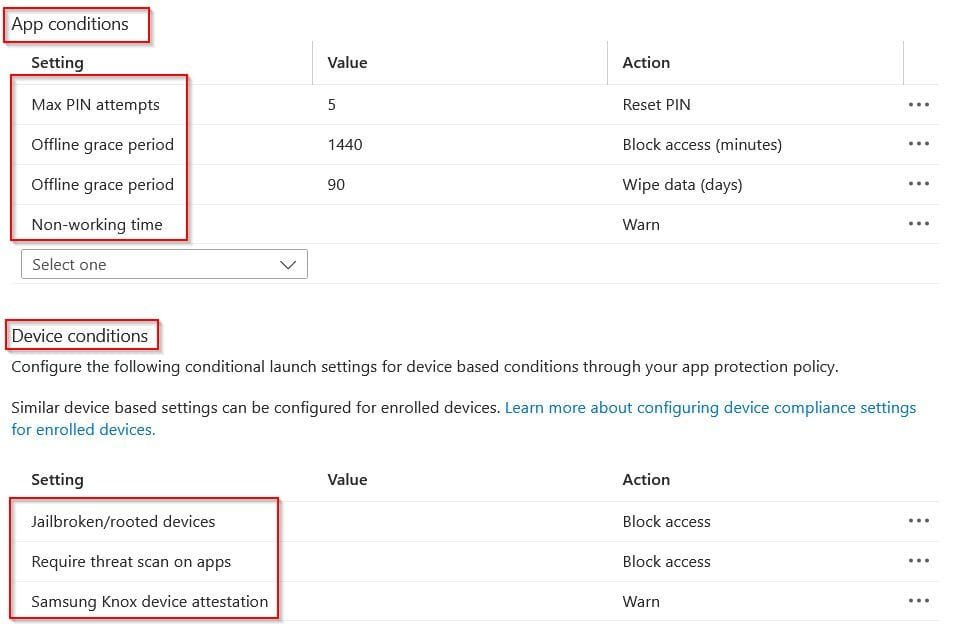
Set PIN Access for Corporate Apps (e.g. 8 PIN with Biometrics enabled or disabled)

Enable Access Requirements, such as enforcing PIN codes or biometric authentication.
Set Conditional Launch (e.g. allow some Android Manufacturers or enforce Samsung KNOX Attestation)
4. Assign the Policy – Assign the policy to a specific USER GROUP within your organization.
Assignment should be including Managed App filter which specify what type of Device Management should include or exclude “assigned User group”
Managed Filter is NOT mandatory but should be used to enhance assignment. Managed filters can be configured through Intune Admin Portal, Apps, Filters, Add Managed App Filter.
Below are few examples for Android Filter Configuration:
Filter can be targeted to include all Android Platforms (Managed and Unmanaged)
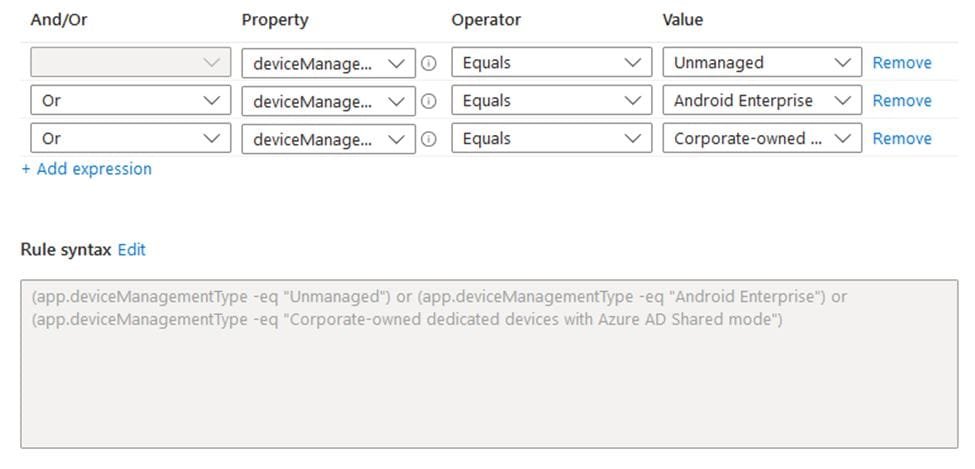
Or unmanaged devices only
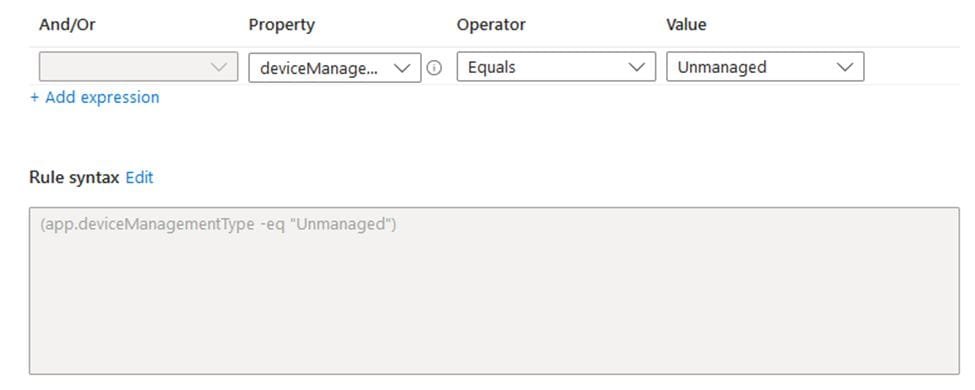
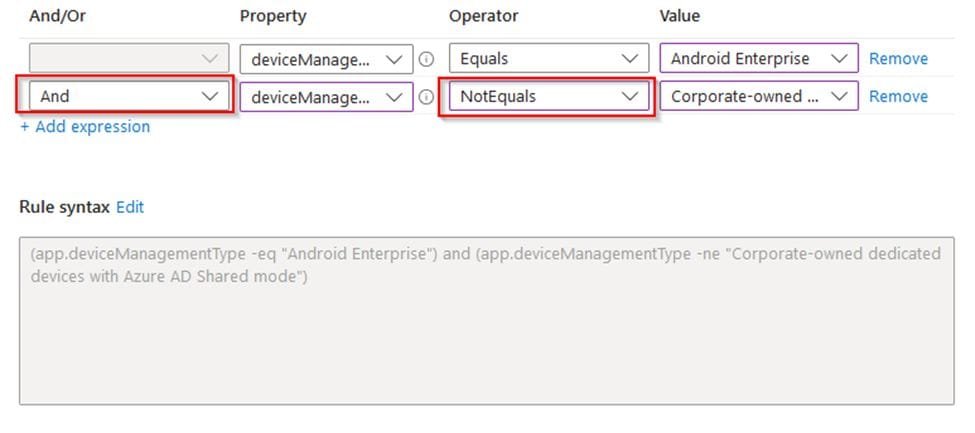
Or Android Enterprise only (Corporate and Personal Android Enrollment except Dedicated Azure AD Shared Mode)
4. Broker, what’s that mean?
For APP t work with Android Device (regardless who is the manufacturer), a Broker APP MUST be installed to be mediant between the App and Microsoft Intune (e.g. synchronize the APP Policy and enforce it to Protected Apps, collect Logs and telemetry data from Apps)
Broker for APP is the Company Portal App.
- Enrolled Devices: Android Enterprise Corporate Enrollment (Fully Managed, Corporate Owned with Personal Profile or Dedicated Devices Azure AD Shared Mode) will have Company Portal App installed by default but will remain in Disabled Mode.
Users will not have any option to start the App. It’ll start silently when the APP is assigned to one of the Corporate Apps and User launches this App.
- Enrolled Devices: Android Enterprise Personal Owned Work Profile.
Company Portal App already installed and when users start any App targeted with APP, Company Portal will Synchronize the Policy in Background. - Non-Enrolled Devices: User MUST install Company Portal App and Don’t sign in to it.
5. End-User Experience
- User Install Company Portal App and then launch Corporate App (for example Outlook)
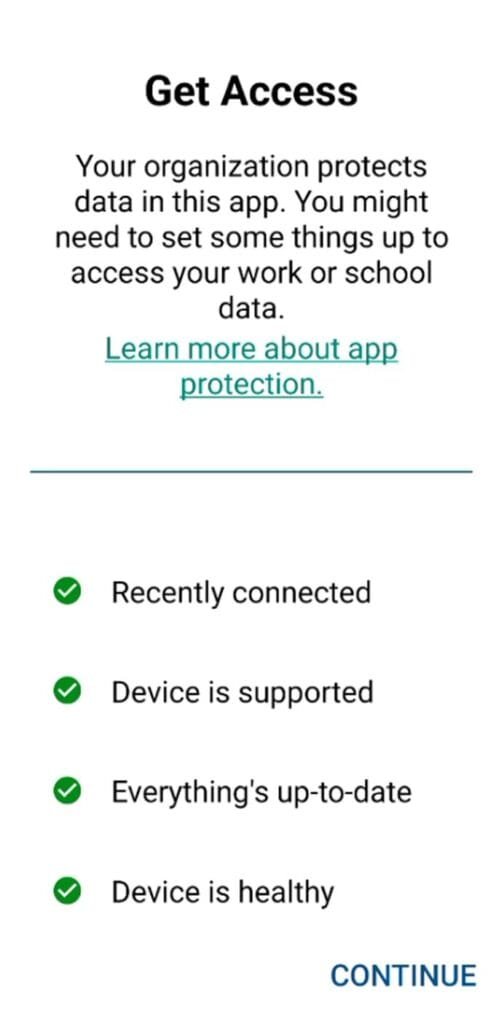
- After completing sign-in to the App, Application Protection Policy will immediately synchronized to Outlook App via Company Portal App and check 4 items
- Recently Connected: User is not Disabled and enabled for Microsoft Services.
- Device is Supported: and not blocked via conditional launch
- Everything is up to date: Intune App SDK, App Version or Company Portal Version
- Device is Healthy: have the latest Google Play Attestation Service, Samsung KNOX Attestation, not Rooted Device.
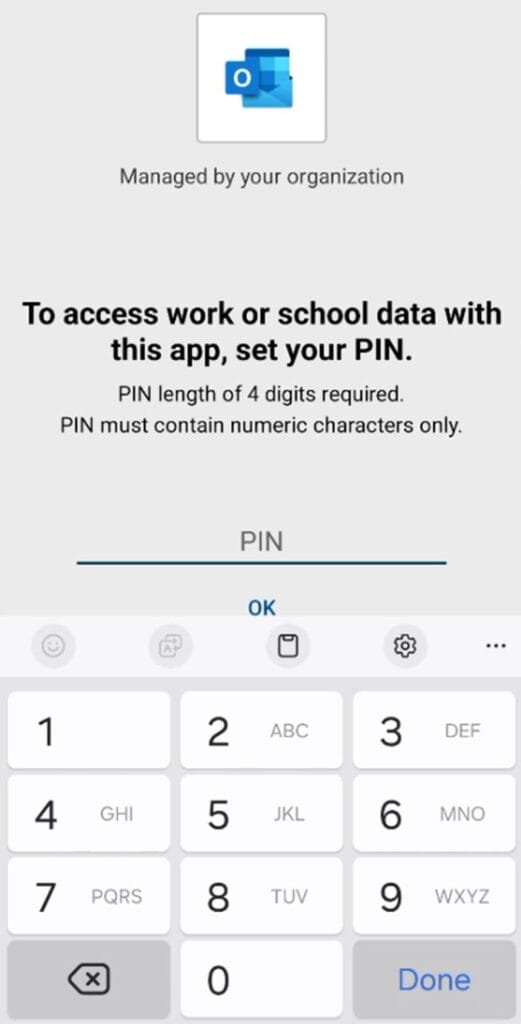
Then user will enforced to enter PIN if it’s configured in “Access Requirement”
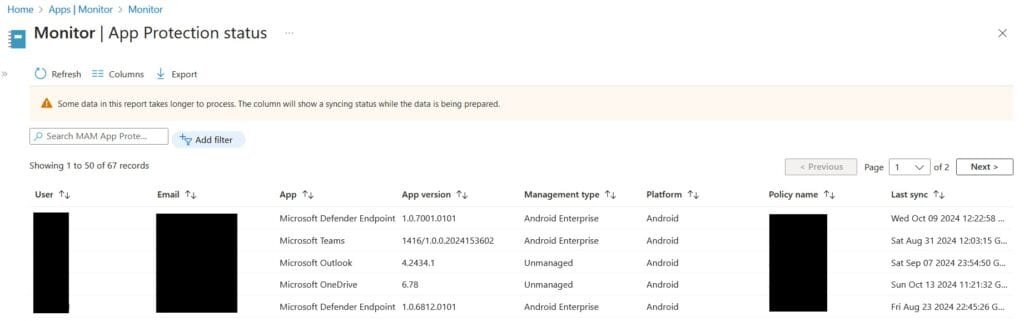
6. How to monitor APP Status?
Monitoring APP for Admin is applicable via Intune Portal, Apps, monitor, App Protection Status
from Column, select all needed fields needed to show in report
Or from “add filter” you can make the report results more filtered per user, policy, app… etc.
Recommending to read article App Protection Article for iOS






Leave a Reply